Data governance can play a pivotal role in making your data work for you. As organizations transition from Excel spreadsheets or outdated facilities management systems to robust Integrated Workplace Management Systems (IWMS) where all facilities data can be logged, tracked and scrutinized, the importance of data governance becomes even more essential. The journey, while challenging, offers significant benefits including reduced risks, lower maintenance costs, and more accurate budgeting.
Table of Contents
- What is Data Governance?
- Benefits of Data Governance
- Understanding the Data Maturity Model
- The Journey to Robust Data Governance
What is Data Governance?
Data governance is the process of managing and protecting an organization's data to ensure its accuracy, security, and proper usage. It involves setting policies, defining roles, and implementing standards to maintain data integrity and compliance. A strong data governance framework helps organizations make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and safeguard sensitive information
Benefits of Data Governance
As organizations enhance their data governance practices, they experience several key benefits:
- Reduced Risks: Improved data governance reduces the risk of data breaches, inaccuracies, and compliance issues. By ensuring that data is accurate, secure, and consistently managed, organizations can mitigate potential risks and protect their assets.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Effective data governance leads to more efficient facilities maintenance. Accurate data allows for better planning and scheduling of maintenance activities, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of assets.
- More Accurate Budgeting: With reliable data, organizations can create more accurate budgets and forecasts. This enables better financial planning and resource allocation, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved financial performance.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: High-quality data provides a solid foundation for decision-making. With accurate and timely information, leaders can make informed decisions that drive organizational success.
- Improved Compliance: Strong data governance ensures that data management practices comply with relevant regulations and standards. This reduces the risk of legal issues and enhances the organization's reputation.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Streamlined data processes and standardized practices lead to greater operational efficiency. This allows organizations to focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down by data management challenges.
Understanding the Data Maturity Model
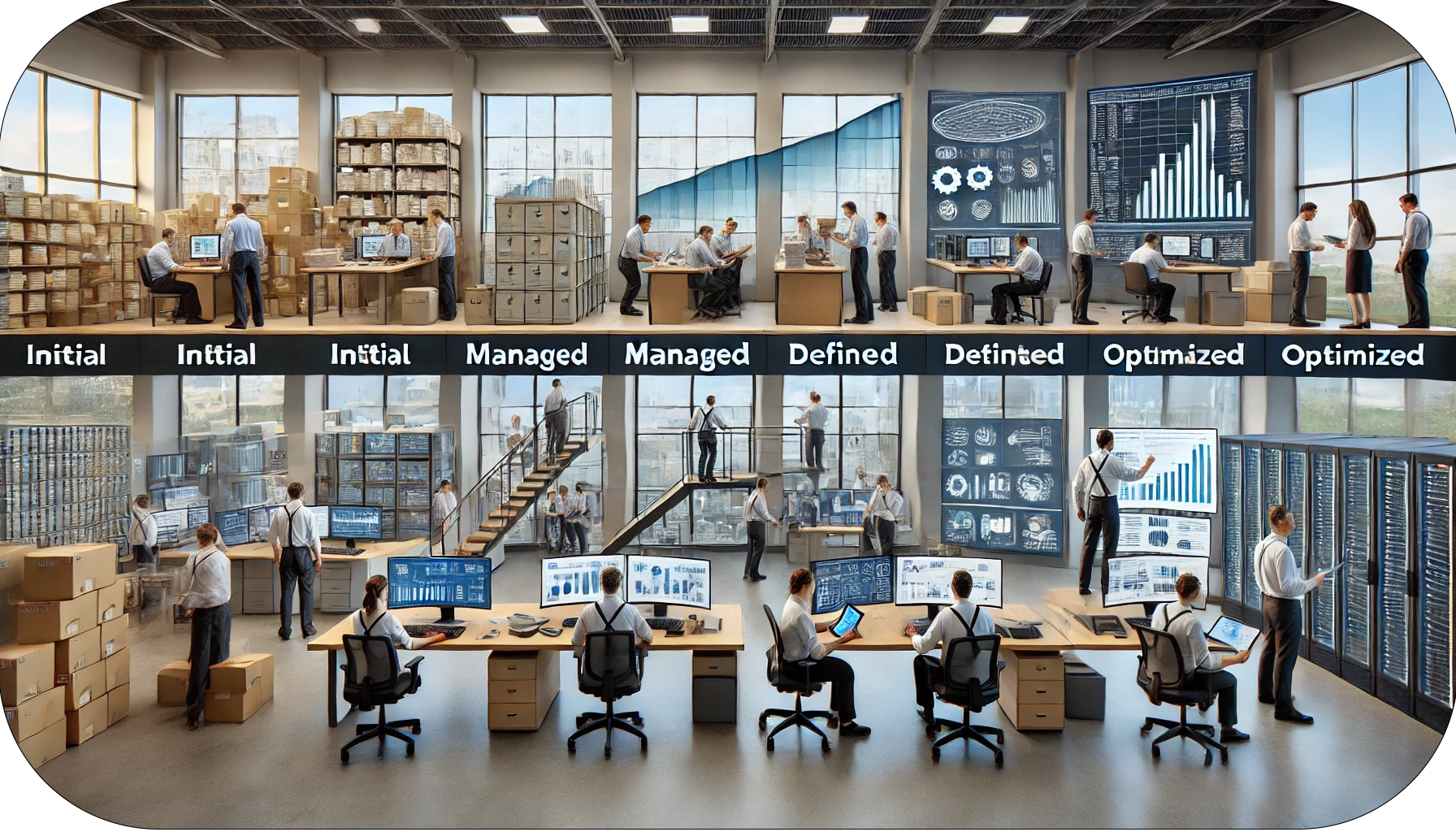
The data maturity model helps organizations figure out how well they manage their data and what they can do to improve. Think of it like a journey—starting from scattered, messy data and moving toward a well-organized, strategic system that drives smart decisions.
Now that we understand what the data maturity model is, let’s apply it to asset data. This is what asset data could look like at each stage of the Data Maturity model:
1. Initial Stage – Data Chaos
- What It Looks Like: Asset condition data is scattered, inconsistent, and largely unrecorded. Inspections may be done manually with paper reports, and there’s little structure for tracking repairs or replacements.
- Benefits: There is no complex system to manage, making operations simple for teams unfamiliar with digital tools.
- Consequences: Data inaccuracies lead to unexpected asset failures, inefficient resource allocation, and costly emergency repairs.
2. Managed Stage – Basic Organization
- What It Looks Like: Some standardization begins—perhaps spreadsheets or a basic database track inspection results and maintenance schedules. However, data quality issues still exist due to manual entry, inconsistent reporting and siloed information.
- Benefits: Better visibility into asset conditions, leading to some preventive maintenance efforts.
- Consequences: Limited oversight, errors from human data entry, and difficulty analyzing long-term trends in asset conditions.
3. Defined Stage – Formal Governance
- What It Looks Like: A structured system for recording and monitoring building assets is in place. Inspections follow standardized procedures, and reporting tools help ensure consistency across teams.
- Benefits: Improved reliability of asset condition data allows for proactive maintenance and better decision-making regarding repairs and replacements. Once the systems are in place, administrative overhead, building and asset maintenance costs savings start to materialize.
- Consequences: Some resistance to new processes, and initial implementation may require significant training and investment.
4. Quantitatively Managed Stage – Data-Driven Insights
- What It Looks Like: Condition assessments are integrated into a centralized system with automated alerts and predictive analytics. Maintenance schedules are optimized based on actual asset performance rather than fixed intervals.
- Benefits: Reduced operational costs, better budgeting, and fewer unexpected failures since repairs and replacements are strategically planned.
- Consequences: Requires ongoing data management oversight, and reliance on data accuracy becomes critical to maintaining efficiency.
5. Optimized Stage – Strategic Decision-Making
- What It Looks Like: Condition assessment data is embedded in daily operations, leveraging AI and machine learning to predict failures before they occur. Real-time monitoring enables informed asset investment decisions, extending building lifespan.
- Benefits: Maximum efficiency, cost savings, improved safety, and sustainable asset management.
- Consequences: High reliance on technology—if systems fail, teams must have backup strategies in place.
The Journey to Robust Data Governance
For many organizations, transitioning to a robust IWMS from Excel spreadsheets or inadequate systems is a significant undertaking. It takes time to get it right, and the focus should be on continuous improvement. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Identify a Data Governance Champion: Appoint a dedicated individual or team to evangelize the importance of data governance. This champion will advocate for accurate information, promote best practices, and ensure that data governance remains a priority.
- Develop a Data Governance Framework: Establish clear policies, procedures, and standards for data management. This framework should outline roles and responsibilities, data quality metrics, and processes for data validation and correction.
- Invest in Training and Education: Ensure that all stakeholders understand the importance of data governance and are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge. Regular training sessions and workshops can help reinforce best practices and keep everyone aligned.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize advanced tools and technologies to support data governance efforts. A robust IWMS can provide the necessary infrastructure for data integration, validation, and reporting, making it easier to manage and leverage data effectively.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Data governance is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Regularly review and refine your data governance practices to ensure they remain effective and aligned with organizational goals.
Would you like to learn more?
Related Resources:
- Facilities Management Overview
- What is the Best IWMS Software for Government?
- The State of Alaska Tackles Statewide Deferred Maintenance
- Why Capital Budgeting Software is Critical in Government Facilities
- Three Keys to Effective Space Management
- Facilities System Integration
- FacilityForce's IWMS Solution